Land, Resources & Natural Regions
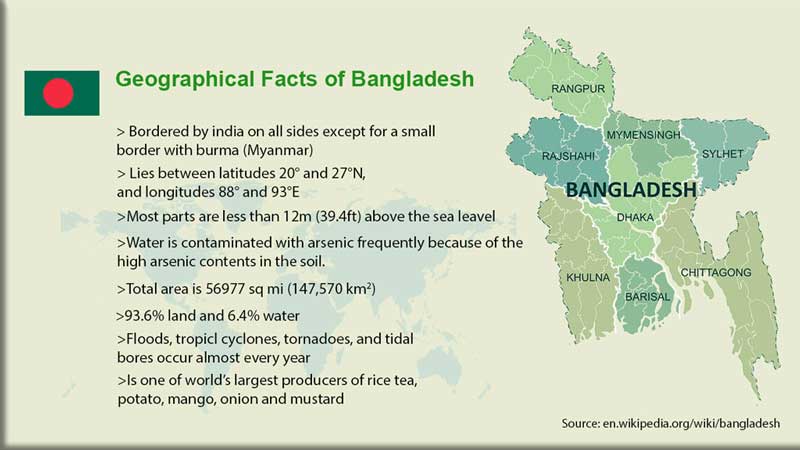
Most of Bangladesh lies within the broad delta formed by the Ganges and Brahmaputra rivers and is exceedingly flat, low-lying, and subject to annual flooding. Much fertile, alluvial soil is deposited by the floodwaters. The only significant area of hilly terrain, constituting less than one-tenth of the nation's territory, is the Chattogram Hill Tracts District in the narrow southeastern panhandle of the country. There, on the border with Myanmar, is Mowdok Mual (1,003 m/3,291 ft), the country's highest peak. Small, scattered hills lie along or near the eastern and northern borders with India. The eroded remnants of two old alluvial ...
See More
Bangladesh Economy
Bangladesh is an agricultural country. With some three-fifths of the population engaged in farming. Jute and tea are principal sources of foreign exchange. Major impediments to growth include frequent cyclones and floods, inefficient state-owned enterprises, inadequate port facilities, a rapidly growing labor force that cannot be absorbed by agriculture, delays in exploiting energy resources (natural gas), insufficient power supplies, and slow implementation of economic reforms. Economic reform is stalled in many instances by political ...
See More